This article is intended for cPanel hosting users who want to monitor and manage their account’s disk space usage.
cPanel includes a built-in Disk Usage feature that helps you quickly identify which directories and files are using the most storage space in your hosting account. This guide shows how to access and interpret the Disk Usage page to efficiently manage your storage.
Step 1: Log in to cPanel
To get started, log in to your cPanel account. For help logging in, see our guide:
Accessing your hosting control panel (cPanel)
Step 2: Open the Disk Usage Interface
Once inside cPanel:
This will bring you to the Disk Usage page, where you can review detailed information about how your storage is being used.
Understanding the Disk Usage Summary
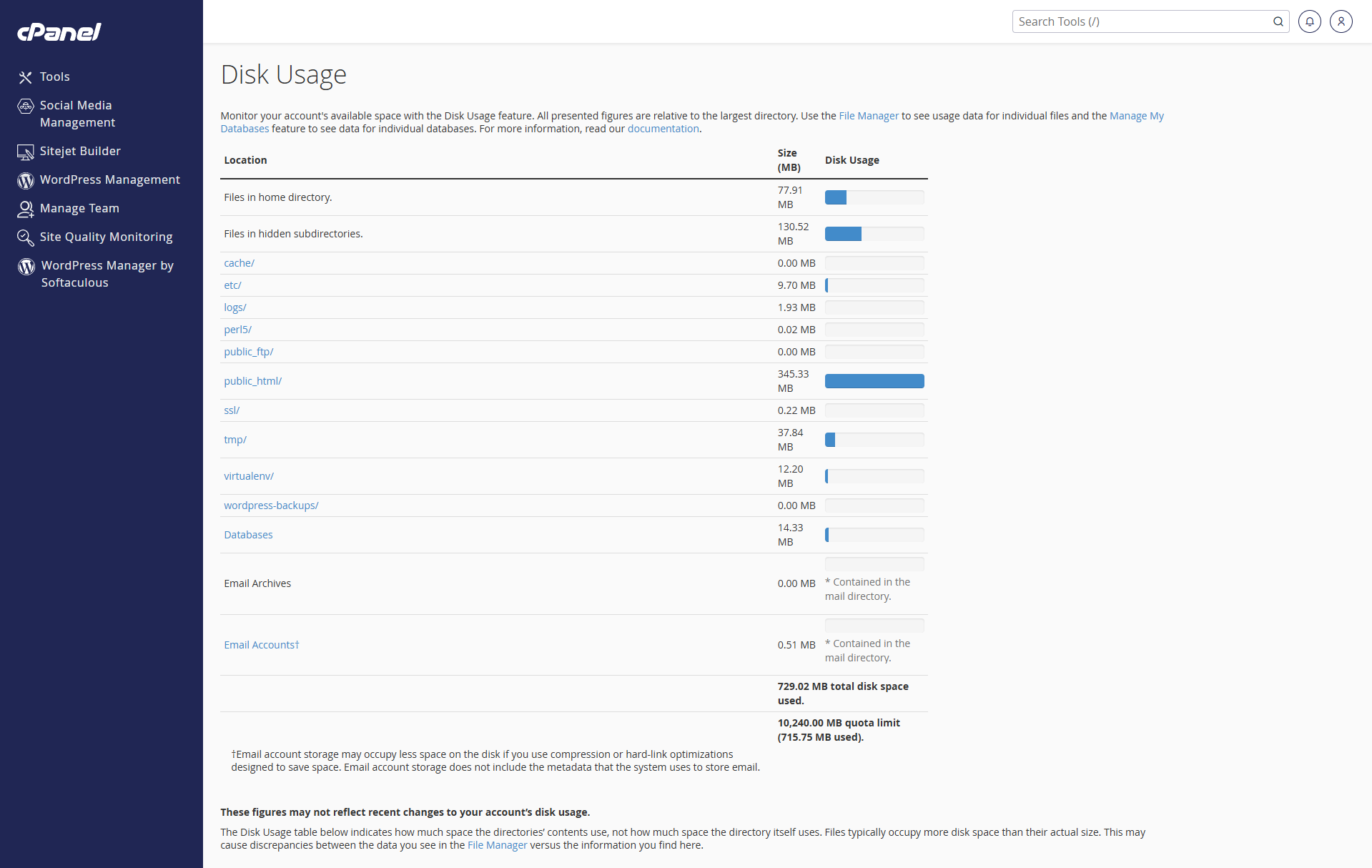
At the top of the Disk Usage page, you’ll see a summary of how much disk space is used in various locations across your account.
📷 Example:
Key areas to check:
-
public_html/ – This is the main web root for your website and often the largest directory.
-
tmp/ – Stores temporary files (e.g. session data or caching files).
-
logs/ – Contains raw access and error logs.
- wordpress-backups/ and softaculous_backups/ – Backups stored by the WordPress Management tool and Softaculous.
At the bottom of the page, you’ll also see your total disk usage, your quota limit, and how much of it has been used.
Step 3: Use the Tree View to Sort by Usage
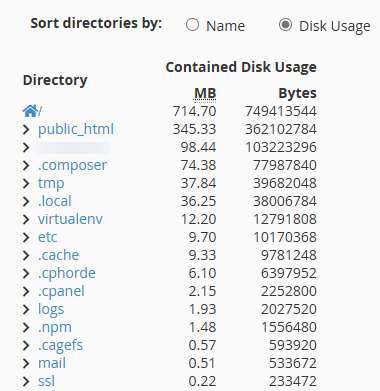
Scroll down further on the same page and you’ll find a Tree View showing all directories sorted by disk usage.
📷 Example:
This view allows you to:
-
Sort directories by size to find what is consuming the most space.
-
Expand each directory to reveal subdirectories and their sizes.
-
Identify hidden or system folders (like
.composeror.npm) that may have unexpectedly high usage.
Step 4: Free Up Space
Once you’ve identified large directories:
-
Click on the directory to open it in the File Manager and remove unnecessary files.
-
Check for:
-
Old backups in
public_htmlorwordpress-backups -
Cached files in
tmpor.cache -
Old logs in
logs
-
-
Consider downloading old backups to your local device and deleting them from the server.
Tips & Notes
-
Disk usage data may not reflect changes made in the last few minutes.
-
Email disk usage is included under
mail/, but metadata storage isn’t always included in the total. -
Files often take up slightly more disk space than their actual size due to how storage blocks are allocated.
If you need help interpreting your disk usage or reducing space, feel free to contact our support team.
Updated by SP on 06/06/2025